Combining Multi-Sequence and Synthetic Images for Improved Segmentation of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiac MRI
On 23 January, our partners University of Barcelona, Universitat Pompeu Fabra and Queen Mary University of London published – among others – the article “Combining Multi-Sequence and Synthetic Images for Improved Segmentation of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiac MRI” as part of the conference proceedings of the International Workshop on Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart 2019 (STACOM 2019).
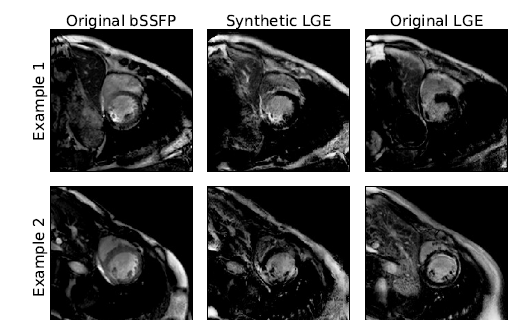
Accurate segmentation of the cardiac boundaries in late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance images (LGE-MRI) is a fundamental step for accurate quantification of scar tissue. However, while there are many solutions for automatic cardiac segmentation of cine images, the presence of scar tissue can make the correct delineation of the myocardium in LGE-MRI challenging even for human experts. As part of the Multi-Sequence Cardiac MR Segmentation Challenge, the paper proposes a solution for LGE-MRI segmentation based on two components. First, a generative adversarial network is trained for the task of modality-to-modality translation between cine and LGE-MRI sequences to obtain extra synthetic images for both modalities. Second, a deep learning model is trained for segmentation with different combinations of original, augmented and synthetic sequences. Our results based on three magnetic resonance sequences (LGE, bSSFP and T2) from 45 different patients show that the multi-sequence model training integrating synthetic images and data augmentation improves in the segmentation over conventional training with real datasets. In conclusion, the accuracy of the segmentation of LGE-MRI images can be improved by using complementary information provided by non-contrast MRI sequences. The article is downloadable from arXiv.