Radiomics Signatures of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Cardiac MRI: Results From the UK Biobank
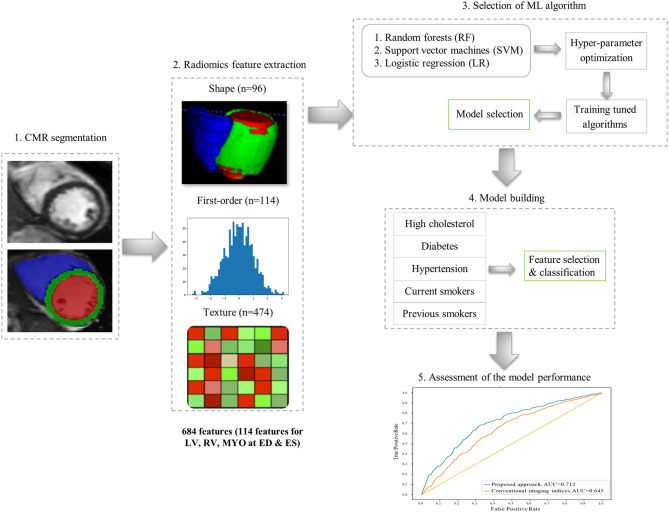
Following previous work pointing out the role of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) radiomics as a novel, valuable technique for advanced cardiac image phenotyping, based on the analysis of multiple quantifiers of shape and tissue texture, this paper assesses the performance of CMR radiomics models for identifying changes in cardiac structure and tissue texture due to cardiovascular risk factors.
The study evaluated five risk factor groups from the first 5,065 UK Biobank participants: hypertension (n = 1,394), diabetes (n = 243), high cholesterol (n = 779), current smoker (n = 320), and previous smoker (n = 1,394). Each group was randomly matched with an equal number of healthy comparators (without known cardiovascular disease or risk factors). Compared to conventional imaging indices, radiomics signatures improved the discrimination of risk factor vs. healthy subgroups and provided some risk-specific signatures with clinical significance. This study confirms the feasibility and potential of CMR radiomics for the characterisation of cardiovascular health and disease, for improved detection and understanding of the early effects of cardiovascular risk factors on cardiac structure and tissue.