Natriuretic Peptides and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Results From the Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe (BiomarCaRE) Consortium
Natriuretic peptide (NP) concentrations are increased in cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) but are associated with a lower diabetes risk. Associations of N-terminal pro-B-type NP (NT-proBNP) and midregional proatrial NP (MR-proANP) with incident type 2 diabetes stratified by the presence of CVD have been investigated.
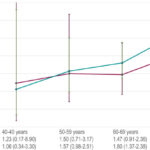
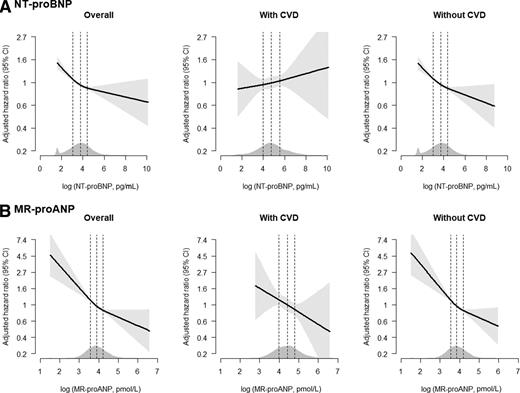
Based on the Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe (BiomarCaRE) Consortium, 45,477 participants with NT-proBNP measurements (1,707 developed type 2 diabetes over 6.5 years of median follow-up; among these, 209 had CVD at baseline) and 11,537 participants with MR-proANP measurements (857 developed type 2 diabetes over 13.8 years of median follow-up; among these, 106 had CVD at baseline) were included. NT-proBNP and MR-proANP are inversely associated with incident type 2 diabetes. However, the inverse association of NT-proBNP seems to be modified by the presence of CVD. Further investigations are warranted to confirm our findings and to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
To read more: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/44/11/2527/138506/Natriuretic-Peptides-and-Risk-of-Type-2-Diabetes